
In today’s global business landscape, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is more than a buzzword – it’s a key driver of success and sustainability.
However, CSR is not a one-size-fits-all concept. Different countries have different expectations and challenges when it comes to CSR. China, as the world’s second-largest economy and a major trading partner for many international businesses, is a prime example. In our latest CSR report, you can find:
- China’s different expectations and regulations for Corporate Social Responsibility
- Development, achievement, and trends of Corporate Social Responsibility in China
- An insightful case study of foreign business Corporate Social Responsibility strategy in China
- Best practices and recommendations on how to develop a Corporate Social Responsibility strategy in China
Summary: Corporate Social Responsibility in China
- Corporate Social Responsibility in China has been evolving in the past two decades.
- CSR in China differs from CSR practices in Europe, with Chinese authorities playing a more prominent role in the process.
- CSR practices in China are closely intertwined with political agendas and policies. Foreign enterprises should therefore keep an eye on government policies in their respective fields.
- Foreign enterprises should align their CSR strategies with China’s sustainability goals, strengthening local relationships, enhancing credibility with government stakeholders, and fostering policy advocacy, thereby maximizing stakeholder engagement and community relations.
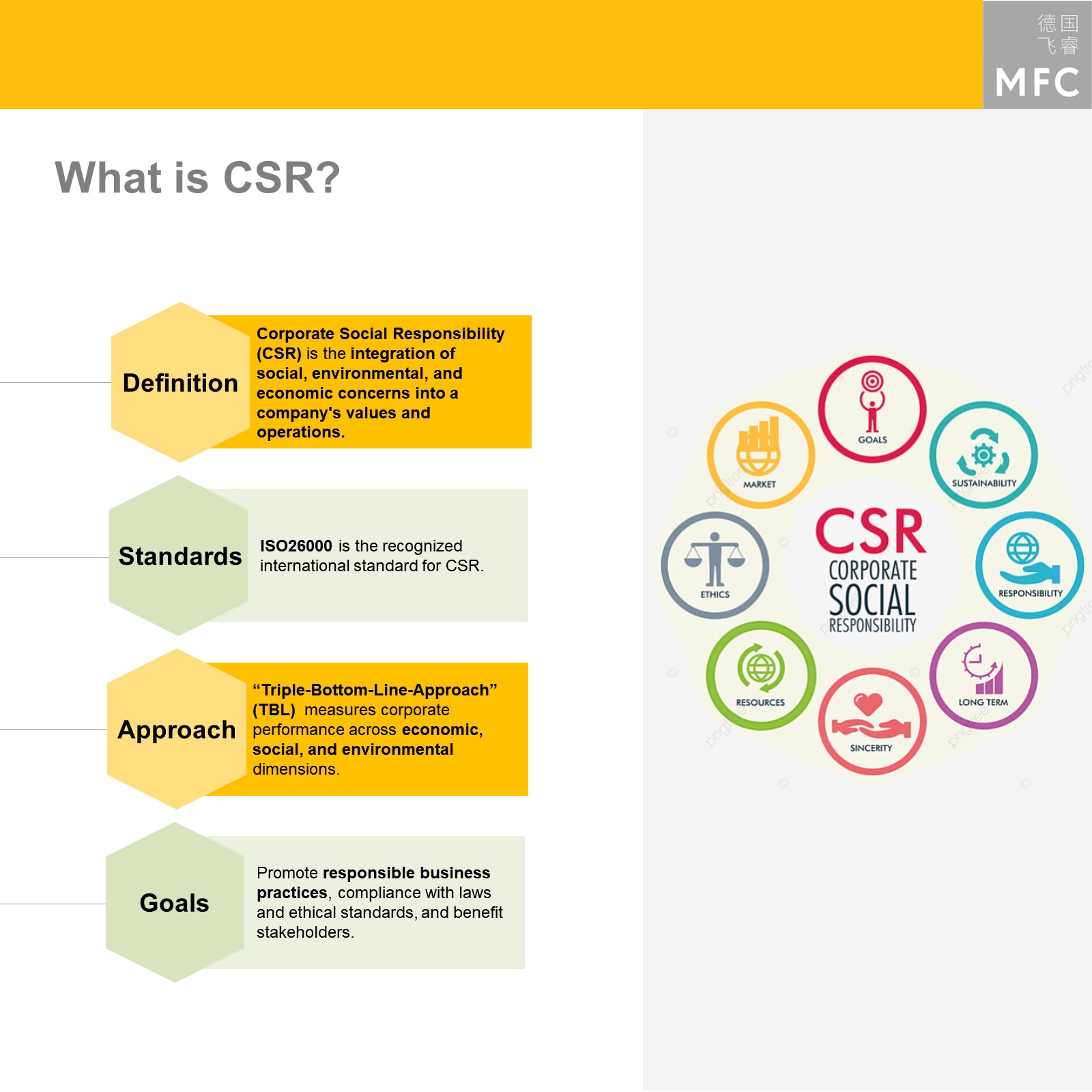
What is Corporate Social Responsibility?
Corporate Social Responsibility is a strategy for businesses, integrating social, environmental, and economic concerns into a company’s values and operations. CSR is a form of self-regulations to ethically orient a company’s business and investment strategies.
By showing the willingness to set a focus on responsible business practices and to comply with laws and ethical standards, the business not only benefits its stakeholders, but also strengthens its brand’s reputation. In the Chinese market, CSR is of particular importance for international businesses to build a strong brand and to prevent possible trouble, such as a brand crisis.


What are the core concepts of Corporate Social Responsibility?
CSR draws on three pillars known as the Triple Bottom Line: profit, people and planet, equaling economic, social, and environmental responsibility. Businesses can therefore only be considered ethically responsible and sustainable if they follow regulations and standards regarding these three factors. The “Triple Bottom Line Approach” therefore measures a business’s performance based on the dimensions.
In 2010, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) released the ISO 26000 standards for businesses and organizations to navigate the CSR landscape. They are not binding standards but offer guidance for ethically responsible conduct. China, as a member of ISO, has adopted these guidelines. The ISO 26000 standards entail seven principles:
- Accountability
- Transparency
- Ethical behavior
- Respect for stakeholder interests
- Respect for the rule of law
- Respect for international norms
- Respect for human rights
These seven principles serve as the underlying roots of socially responsible behavior and form the basis for the seven core subjects relevant to every organization adhering to CSR standards:
- Organizational governance
- Human rights
- Labor practices
- The environment
- Fair operating practices
- Consumer issues
- Community involvement and development
Does China have Corporate Social Responsibility?
Corporate Social Responsibility in China was first introduced into the business landscape in the 1990s. Initially, both enterprises and the Chinese government were cautious about the CSR system. With rising international pressure, both regulatory as well as trade-related, CSR procedures became more popular. Since the mid-2000s, the Chinese government paid increasing attention to CSR-related issues, which facilitated its further adoption in the Chinese business landscape.
The introduction of CSR in China was ultimately a means for the CCP to legitimize its rule and tackle several socio-economic and inequality-related issues facing the country. CSR proved to be valuable for Hu Jintao’s policy constructing a ‘Harmonious Society’ focusing on greater equality while pursuing economic growth and other economic policies like the ‘Scientific Development Concept’.
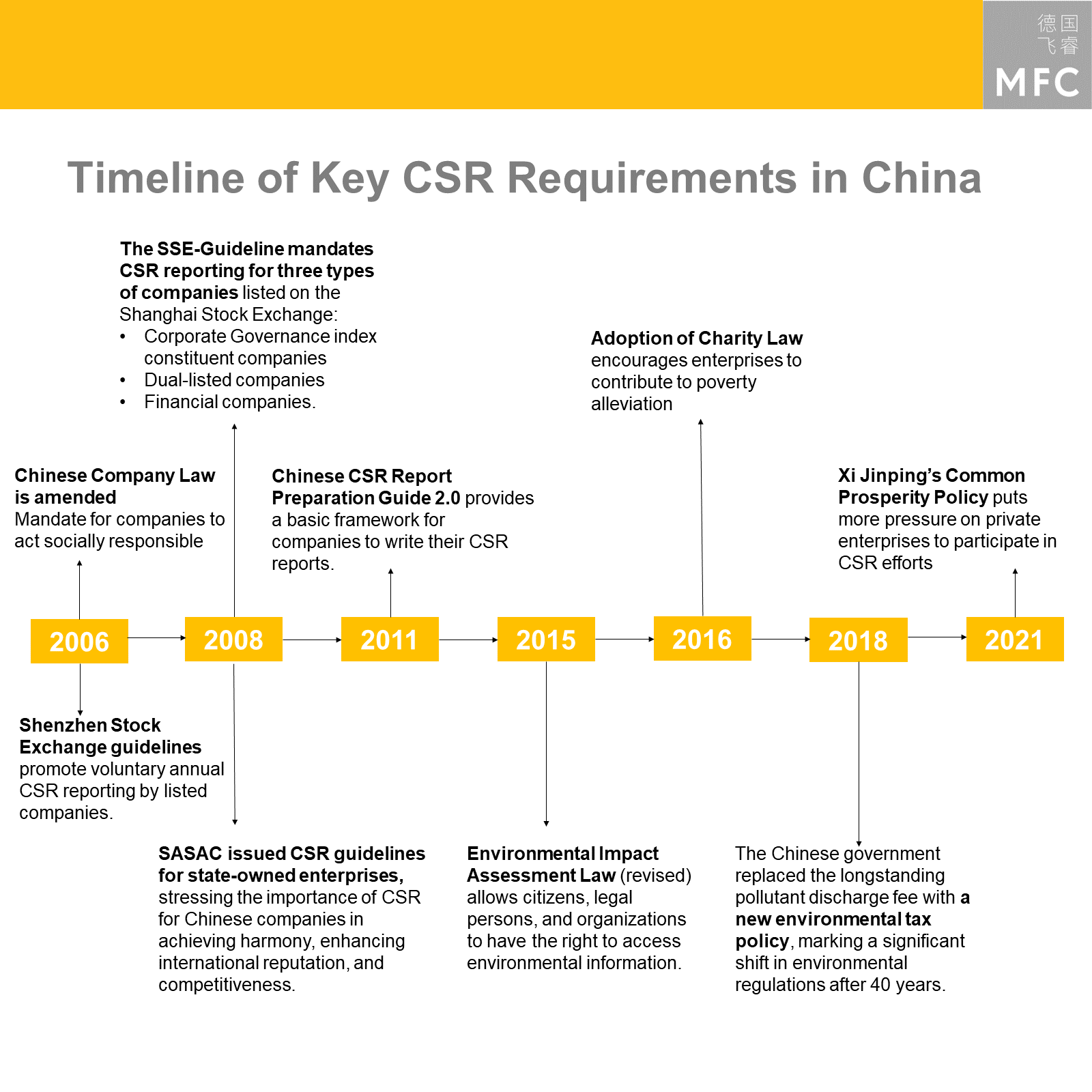
A Timeline of Corporate Social Responsibility in China
In 2006, the Chinese Company Law was amended, explicitly mandating companies to act socially responsible. Following the law, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange provided guidelines for voluntary annual CSR reporting. In 2008, the Shanghai Stock Exchange also listed guidelines concerning CSR practices. In the same year, the state-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC) issued CSR guidelines for Chinese state-owned enterprises (SOEs).
In 2011, the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences published a guide for Chinese SOEs offering a basic framework for CSR-reporting. It served as encouragement for SOEs to report their CSR efforts. With the 2015 revision of the Environmental Impact Assessment Law, citizens and legal entities were now allowed access to environmental information. The Charity Law, encouraging enterprises to contribute to poverty alleviation, was adopted in 2016. In 2018, the Chinese government furthermore replaced the longstanding pollutant discharge fee with a new environmental tax policy. Xi Jinping’s ‘Common Prosperity’ policy from 2021 puts more political pressure on private enterprises to actively participate in the campaign and thereby increase participation in CSR efforts.
What are China’s different regulations for Corporate Social Responsibility?
CSR in China is closely connected to political agendas and policies. Researcher Jie Zeng
argues, that the Chinese government itself has been the biggest promoter of CSR – serving as a response to popular discontent. In China, CSR corresponds with policies such as the construction of a “harmonious society”, as well as with Xi Jinping’s “poverty alleviation” and “rural revitalization” programs. In contrast to other countries, pressure by Chinese civil society regarding CSR is limited. NOTE: this last sentence is unclear. What do we mean? If you tell me what we are trying to say I can help to reword it.
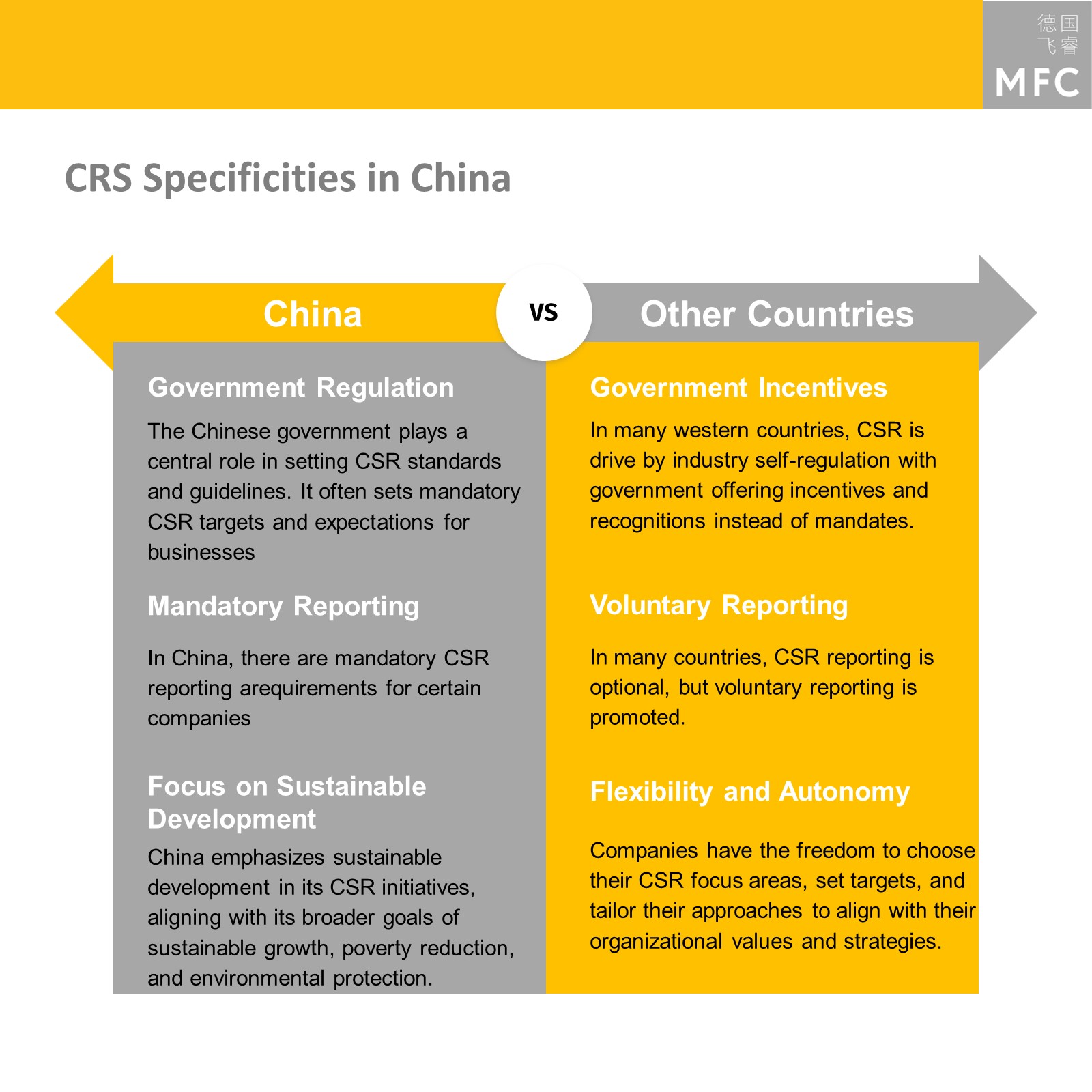
China has different expectations and regulations for Corporate Social Responsibility. Despite both SOEs and private companies applying international CSR practices and standards, there are several differences in CSR regulations in China that need to be considered:
- Government regulation in Chinese CSR practices: The Chinese government plays a central role in setting CSR standards and guidelines. It often sets mandatory CSR targets and expectations for businesses. This strict top-down approach differs from CSR practices in other countries. In many western countries CSR is driven by industry self-regulation, with governments offering incentives and recognitions instead of mandates.
- Mandatory CSR reporting in China: According to the Chinese Company Law, CSR disclosure is mandatory for certain enterprises operating in China since 2006. Legally incorporating CSR in Chinese laws is therefore another distinct characteristic of CSR in China.
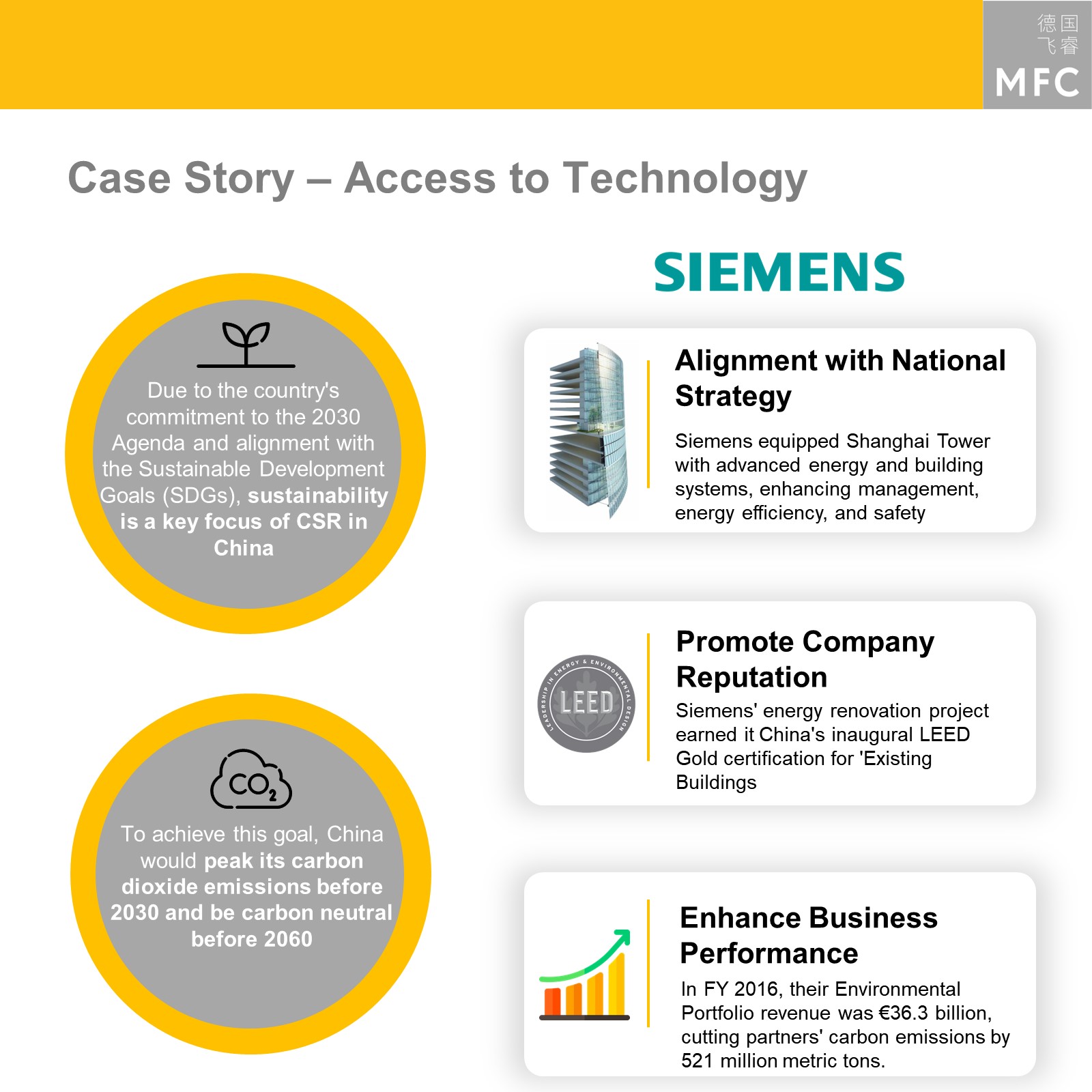
- Focus on sustainable development in Chinese CSR initiatives: China emphasizes sustainable development in its CSR initiatives, aligning with its broader goals of sustainable growth, poverty reduction and environmental protection.
- CSR in China as incubator for strengthened relations between businesses and Chinese authorities: Since local authorities are responsible for a considerable amount of resource allocation, Chinese companies use CSRefforts to strengthen their relationship with local authorities and help their business’s development. A successful cooperation in social, economic, and ecological aspects is, on the other hand, helpful for the local authorities’ implementation of related policies.
CSR in China: Best Practices and Recommendations
Foreign enterprises should align their CSR strategies with China’s sustainability goals, strengthening local relationships, enhancing credibility with government stakeholders, and fostering policy advocacy, thereby maximizing stakeholder engagement and community relations.
- Understand Regulations: Familiarize yourself with China’s laws and regulations related to CSR, environmental protection, labor rights and community engagement. Compliance with local laws is crucial for a successful CSR strategy.
- Community Engagement: Engage in community development projects, philanthropy, and volunteer activities that positively impact the local communities where you operate. Build partnerships with local organizations and contribute to social causes.
- Environmental Focus: CSR initiatives in China often revolve around reducing pollution, promoting resource conservation, and adopting eco-friendly practices to address environmental concerns.
- Sustainable Development: Sustainable development has gained strategic importance in China, as emphasized by President Xi at the International Economic Forum in Russia, where he described it as the “golden key” to addressing global challenges.
- Stakeholder Management: Chinese consumers, employees, communities, investors, and government authorities have higher expectations for responsible business practices.
- Supply Chain Management: In China, responsible supply chain management is another key CSR focus, with businesses expected to ensure ethical sourcing, fair labor practices, and sustainable production processes.
- Foster connections to local authorities: Cooperating with local authorities in CSR-related fields like charity or environmental projects strengthens local relations and helps the business’s success.

Case Studies on Corporate Social Responsibility in China:
Siemens and Intel Corporate offer insights in how CSR efforts in China can successfully be integrated in the companies’ China strategy.



Follow us on LinkedIn for more Insights & contact us for expert guidance and support with your CSR projects in China.
